If a stroke happens in this area it can cause changes with speech vision and sensation. This means that clinical syndromes produced by occlusion of a particular vessel are also variable.
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar artery.

. Upper cervical spinal cord. Each artery originates from the first part of the subclavian artery it then courses superiorly along the sides of the neck merging with its companion at the pons level to form the single midline basilar artery. The entire blood supply of the brain and spinal corddepends on two sets of branchesfrom the dorsalaorta.
If the blood supply to the hindbrain via the paired vertebral arteries is reduced sufficiently signs and symptoms of tertebrobasilar ischaemia may result. Lood in the brain is supplied by two pairs of large blood vessels arteries. Gives off a posterior inferior cerebellar artery.
Throughout spinal branches split off at the vertebral foramina to supply various parts of the vertebral bodies the medulla brain region and the posterior inferior cerebellar artery PICA. The vertebral arteriesarise from the subclavianarteries and the internal carotid arteriesare branches of the commoncarotid arteries. It enters the skull through the foramen magnum.
These vessels run along the front of the neck. The posterior inferior cerebellar artery PICA which supplies the inferior aspect of the cerebellum The two vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery which runs on the anterior surface of the pons. Most of the thalamus and hypothalamus.
After this the two vertebral arteries converge to form the basilar artery. Paired vertebral arteries provide blood supply for the upper part of the spinal cord brainstem cerebellum and posterior part of the brain. The angle where vertebral arteries meet the basilar artery vertebrobasilar junction is 46 degrees.
Vertebral arches facet joints dura matter spinal nerve and communicates with the posterior spinal artery. It arises from the confluence of two vertebral arteries at the medullo-pontine junction to ascend through the basilar sulcus on the ventral aspect of the pons. Clinical Relevance edit edit source It lies close to the vertebral bodies and facet joints where it may be compressed.
The selective angiogram of the vertebral artery in the lateral projection reveals the major intracranial branches. The basilar artery is part of the blood supply system for the brain and central nervous system. The carotid arteries and the vertebral arteries.
Its the first and largest branch of the very first part of the subclavian artery. The vertebral and basilar arteries supply the brainstem and cerebellum. Concerning the branches each vertebral artery.
At the base of the brain the carotid arteries and vertebral arteries come together to form the Circle of Willis. It runs behind the carotid artery which is also in the neck. It is formed where the two vertebral arteries join at.
V1 pre-foraminal arises from the subclavian artery. The vertebral artery. The vertebral arteries divide into four segments based on where they are within the spinal column.
The basilar artery terminates by bifurcating into the posterior cerebral arteries. What supplies the vertebral artery. The vertebrobasilar arteries supply the posterior two-fifths of the cerebrum part of the cerebellum and the brain stem.
There is a right-sided carotid and a left-sided carotid artery. Anterior meningeal artery muscular and spinal branches. Circle of willis contains.
2 Central branch lenticulo-striate artery which supply all dorsal surface of internal capsule Vertebro-Basilar artery A Vertebral artery. Arterial Circle of Willis. Contributes to the formation of the anterior spinal artery via tributaries that converge in the midline anterior to the medulla oblongata.
There are several factors that may cause a reduction in vertebral artery blood flow. Posterior inferior cerebellar artery supplies the cerebellum. The basilar artery Latin.
Segmental cervical muscular and spinal branches. Several branches from the basilar artery originate here and go onto supply the cerebellum and pons. Where does the vertebral artery go.
As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system the vertebral arteries provide supply blood to the upper spinal cord brainstem cerebellum and posterior part of brain. It joins its fellow at the lower border of the pons to form the basilar artery. It provides arterial supply to the brainstem.
Cortex and deep white matter of the posterior medial parietal lobes and medial and inferior temporal and occipital lobes. Anterior frontal and posterior occipital lobes. This is a circle of arteries that pro- vide many paths for blood to supply oxygen and nutrients the brain.
An uncompromised blood flow to the brain is essential for normal neurological function. Arteria basilaris contributes to the posterior component of the circle of Willis and supplies the contents of the posterior cranial fossa. Vertebral artery is one of the main arteries at the base of the neck and is the first branch of the subclavian artery.
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery PICA is the largest branch of the vertebral artery and is one of three main arteries supplying the cerebellum. Overview of major regions supplied. Vertebral arteries are responsible for about 30 of the brain blood supply.
The latter of these represents the largest branch and is one of the primary sources of blood to the cerebellum. V2 foraminal travels alongside vertebral veins and nerves. The vertebral arteries arise from the subclavian arteries one on each side of the body then enter deep to the transverse process at the level of the 6th cervical vertebrae C6 or occasionally in 75 of cases at the.
The vertebral artery is among the main arteries which supplies the brain. Morphological characteristics of the first part of the vertebral artery. As the supplying component of the vertebrobasilar vascular system the vertebral arteries supply blood to the upper spinal cord brainstem cerebellum and posterior part of brain.
Posterior part splenium of the corpus callosum. The vertebral arteries gain access to the cranial vault via the foramen magnum anterolateral to the brainstem. Anterior Inferior Cerebellar artery.
Supply edit edit source It supplies 20 of blood to the brain mainly hindbrain along with the internal carotid artery 80. Vertebral body dura matter spinal nerve and communicates with the anterior spinal artery of the spinal chord posterior radicular artery supplies. Posterior cerebral artery PCA What blood vessels supply blood to the brain.
This system provides important areas of the brain with blood. It arises from the 1st part of subclavian artery. What is the function of the vertebral artery.
The vertebral arteries and the ten medullary arteriesthat arise from segmental branches of the aorta provide the primary vascularizationof. The aim of this study was to examine the vertebral arterys course in the first segment and to define the an. Perhaps the most important thing to recognize about the brainstems blood supply is just how variable the vessels can be in size and position but still provide adequate perfusion.
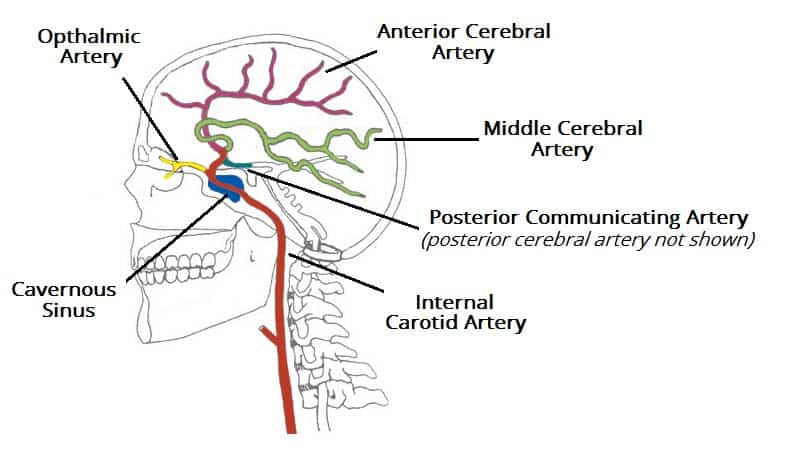
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy
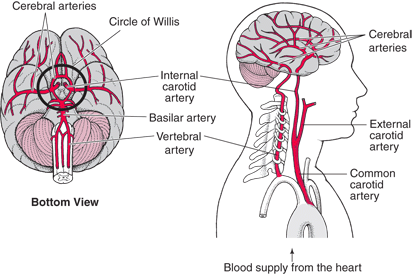
Brain Basics Joe Niekro Foundation

Blood Supply Of The Brain Textbook Of Clinical Neuroanatomy 2 Ed
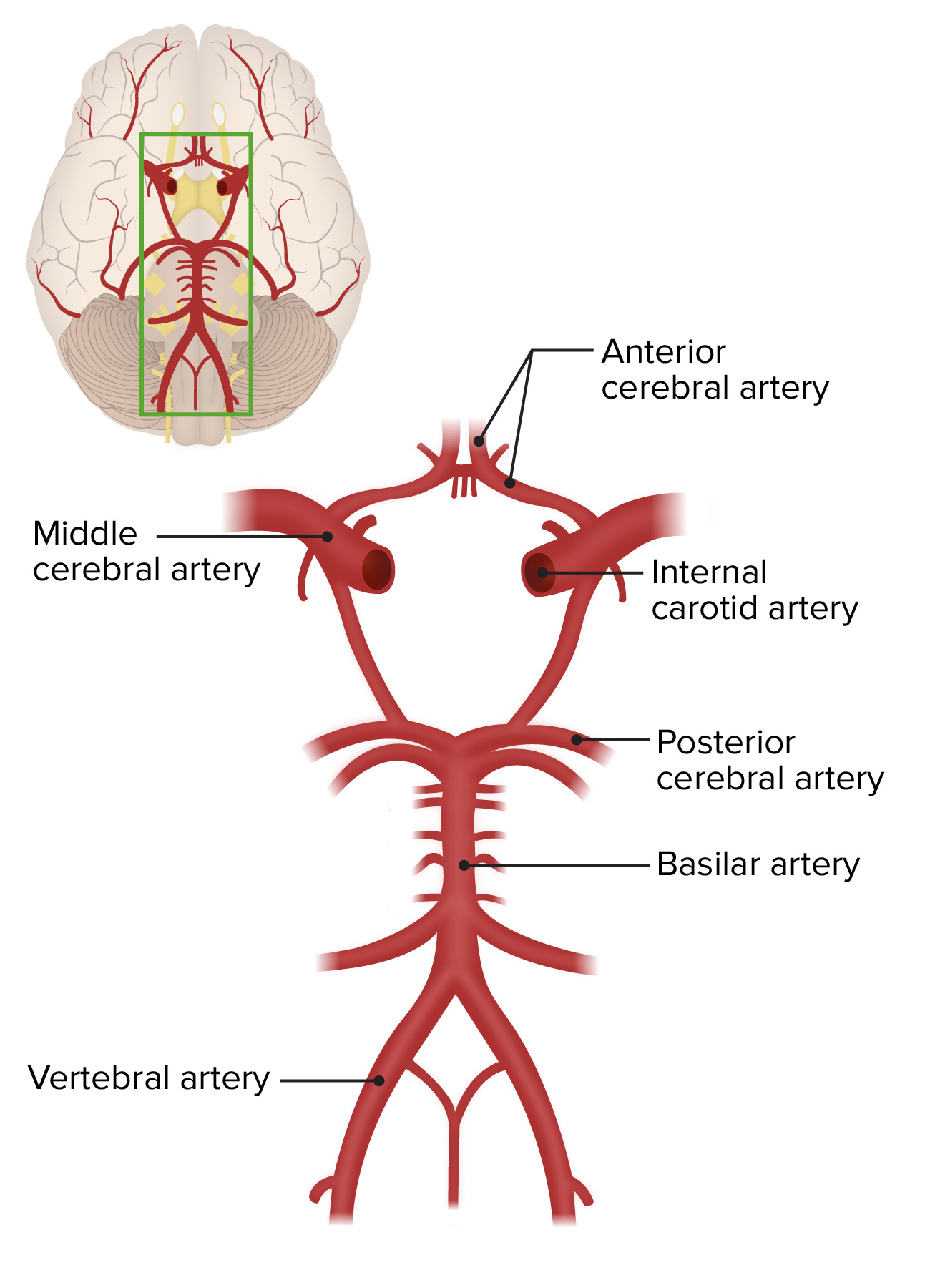
Cerebrovascular System Anatomy Concise Medical Knowledge
Blood Supply Of The Central Nervous System Gross Anatomy Of The Brain Part 1
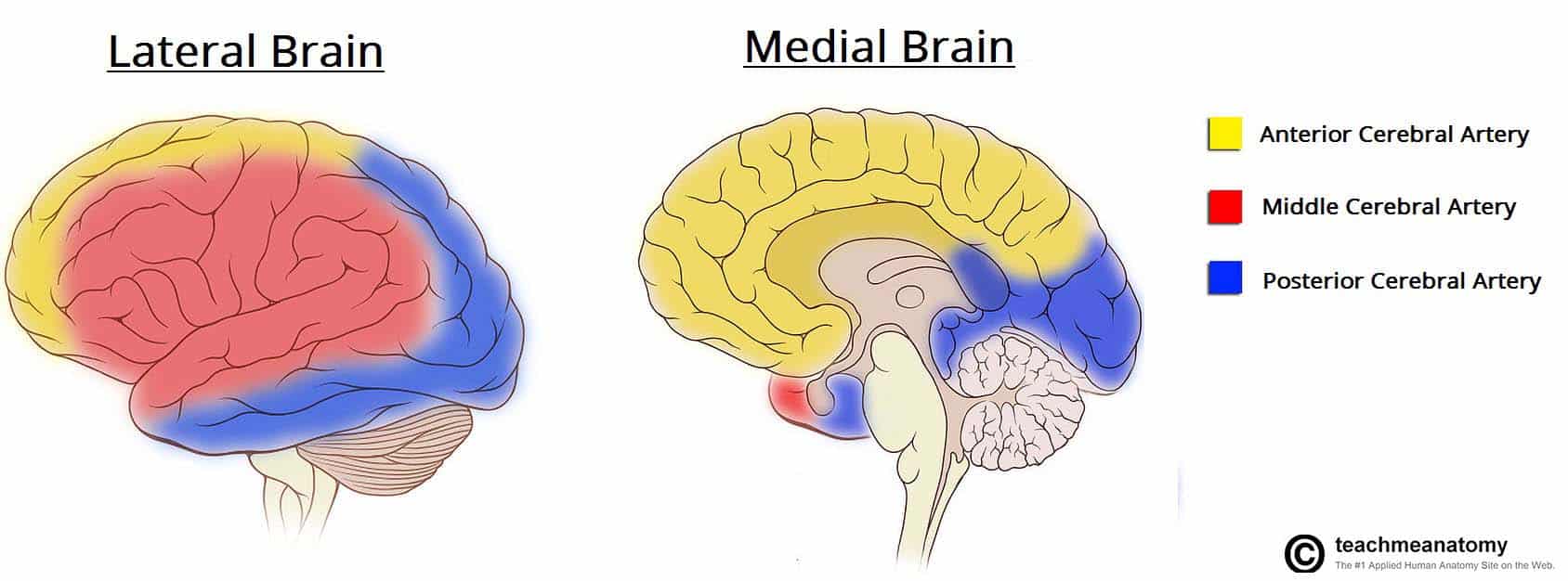
Arterial Supply To The Brain Carotid Vertebral Teachmeanatomy
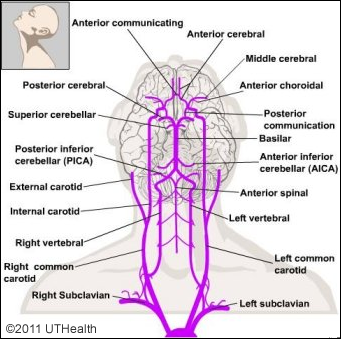
Neuroanatomy Online Lab 4 ƒ3 The Ventricles And Blood Supply Vertebral Basilar System


0 comments
Post a Comment